Using QUBEKit as an API
What is QUBEKit?
QUBEKit is a Python package for the derivation of classical molecular mechanics force field parameters from quantum mechanical data. QUBEKit pulls together multiple pre-existing engines, as well as bespoke methods to produce accurate results with minimal user input. QUBEKit aims to avoid fitting to experimental data where possible while also being highly customisable.
QUBEKit is also easy to use as an Application Programming Interface (API) for two key reasons: the persistent molecule object and the separated stages. By initialising a molecule from a file or SMILES string, it can then be passed to any of the QUBEKit stages to be operated on. The coordinates can be optimised, bond and angle parameters can be calculated, virtual sites can be added, all in the same way. For example, the following code could be used to fit virtual sites to methylisocyanate, given only a pdb file and some charge data from Chargemol:
from qubekit.charges import DDECCharges, ExtractChargeData
from qubekit.molecules import Ligand
from qubekit.nonbonded import VirtualSites
from qubekit.parametrisation import OpenFF
# Load the molecule into QUBEKit from file.
molecule = Ligand.from_file("methylisocyanate.pdb") # Generate basic parameters using OpenFF.
OpenFF().run(molecule)
# Extract charge data and save to be used in the virtual sites fit.
ddec_file_path = "ChargeMol"
ddec_version = 6
ExtractChargeData.extract_charge_data_chargemol(
molecule, ddec_file_path, ddec_version
)
# Apply symmetry to the reference data (optional).
DDECCharges.apply_symmetrisation(molecule) # Fit virtual sites to the molecule.
VirtualSites().run(molecule)
# Write the force field parameters to file.
molecule.write_parameters("methylisocyanate.xml")Here, we can see that a virtual site has been added to the nitrogen atom of methylisocyanate:
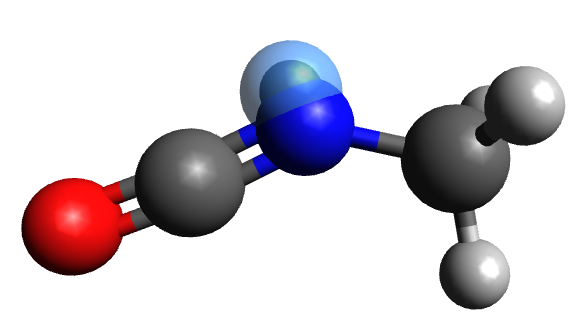
Input files may be downloaded from here.
How to find out more
Check out the QUBEKit docs for more info on how to get the most out of QUBEKit.